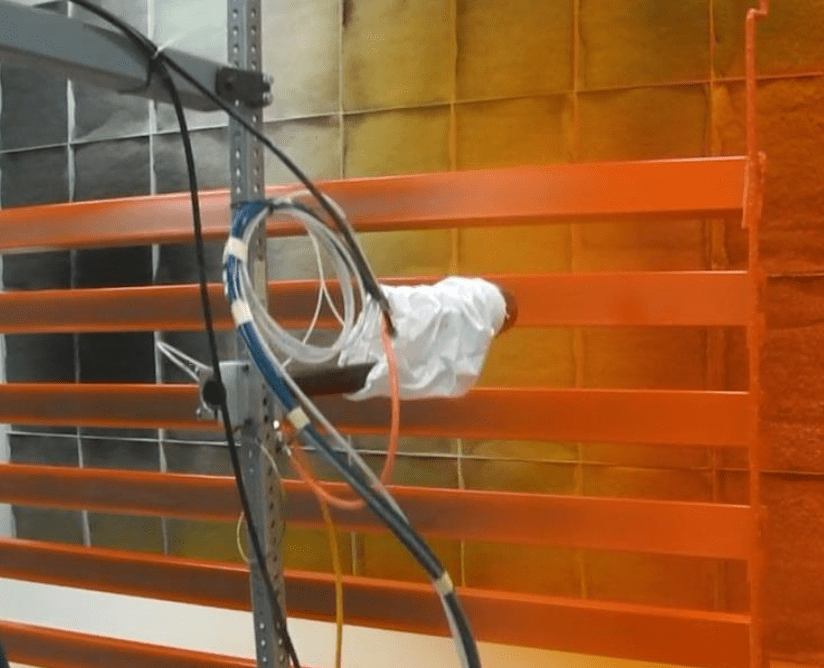
A revolution in colour application: how does electrostatic atomisation work?
Electrostatic atomisation is a groundbreaking technology that drastically increases the application efficiency of paints and coatings. But how does this process work and what advantages does it offer? In this article, we explain the basics and the benefits of electrostatic atomisation.
What is electrostatic atomisation?
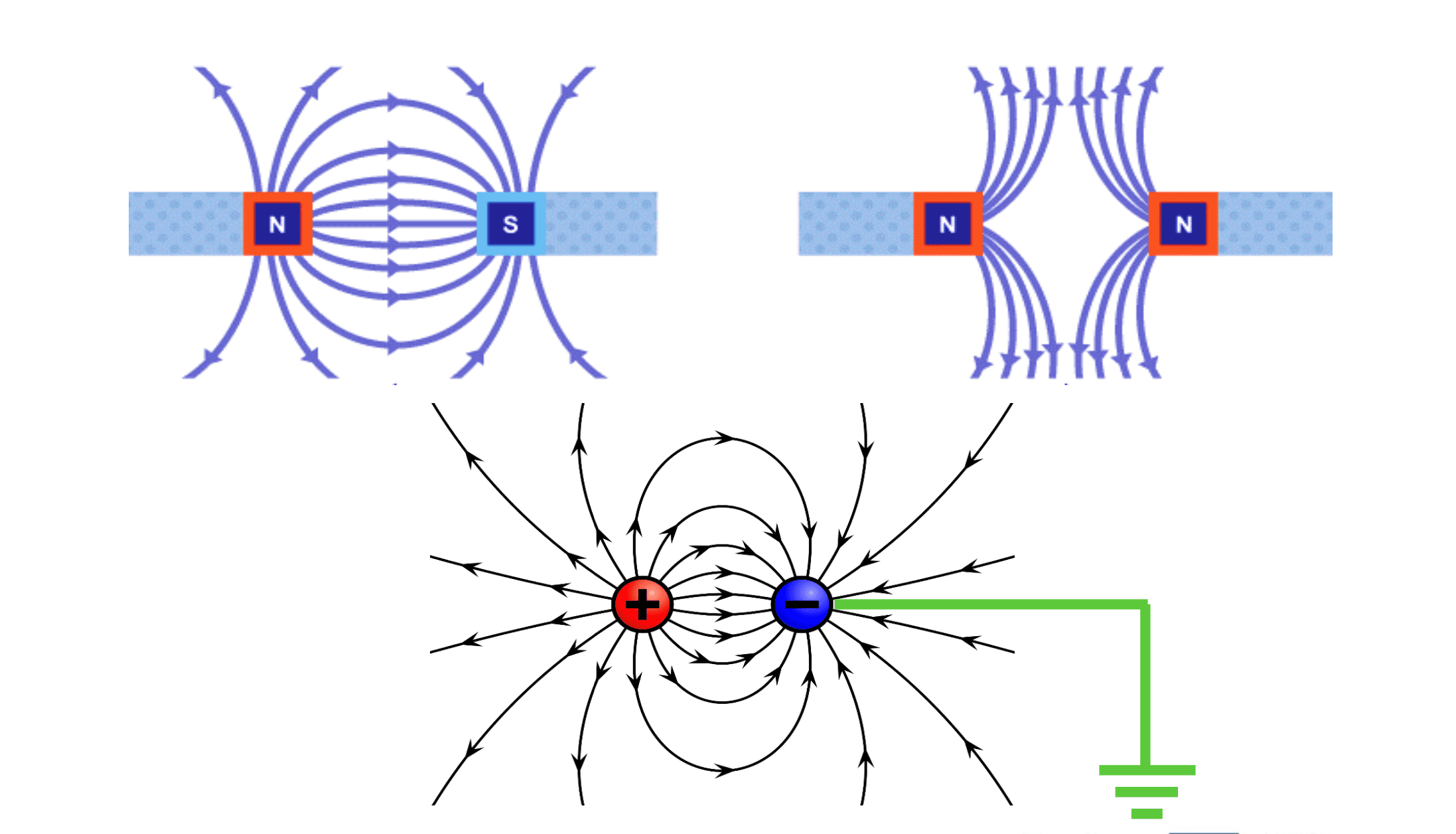
Electrostatic atomisation is a process in which paint or coating materials are applied to a target object using an electrical charge. This process uses the physical property that opposite electrical charges attract each other.
The process in detail:
Particle charging: In the first step, the paint or coating is given an electric negative charge in the spray gun.
Earthing the target object: The object to be coated is earthed, giving it a positive charge and causing it to attract the negatively charged particles.
Attraction: the negatively charged paint particles are drawn directly to the positively charged object by electrostatic attraction, enabling more efficient and precise coating.
Advantages of electrostatic atomisation:
Increased efficiency: the electrostatic attraction causes a higher quantity of paint particles to be deposited on the object, minimising waste.
Better coverage: Even hard-to-reach places and corners can be evenly coated, which is often not possible without electrostatics.
Environmentally friendly: since more paint reaches its target, fewer solvents and paint mists are released into the environment, reducing the process's environmental footprint.
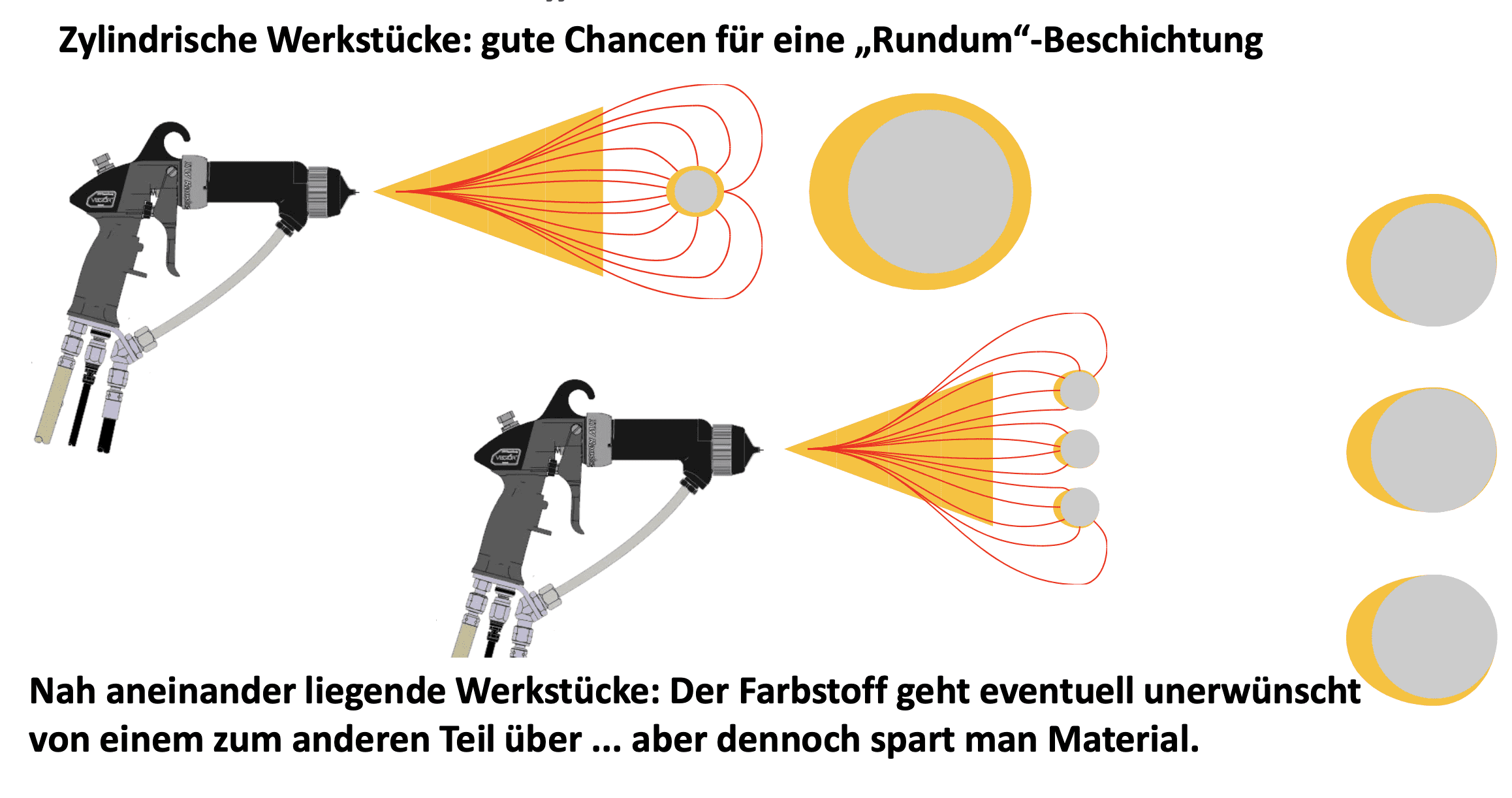
Conclusion:
Electrostatic atomisation is more than just an innovative coating method. It is a sustainable solution that helps to save materials and improve the working environment. This makes it an indispensable tool in modern manufacturing.









